Indoor air quality is critical to our health and well being. Have you ever wondered how important is indoor air quality to your health? We Americans spend on average 90% of our time indoors, with the majority of that time being spent inside our homes. Shockingly, the air we breathe inside of our homes and offices can in fact be more polluted than the air we breathe outside. The US Environmental Protection Agency has found that certain harmful pollutants are 2x to 5x more concentrated inside when compared to the air outdoors.
Given we are spending so much time indoors, it is important to look at indoor air quality and examine the impact it is having our health, comfort and bank accounts.
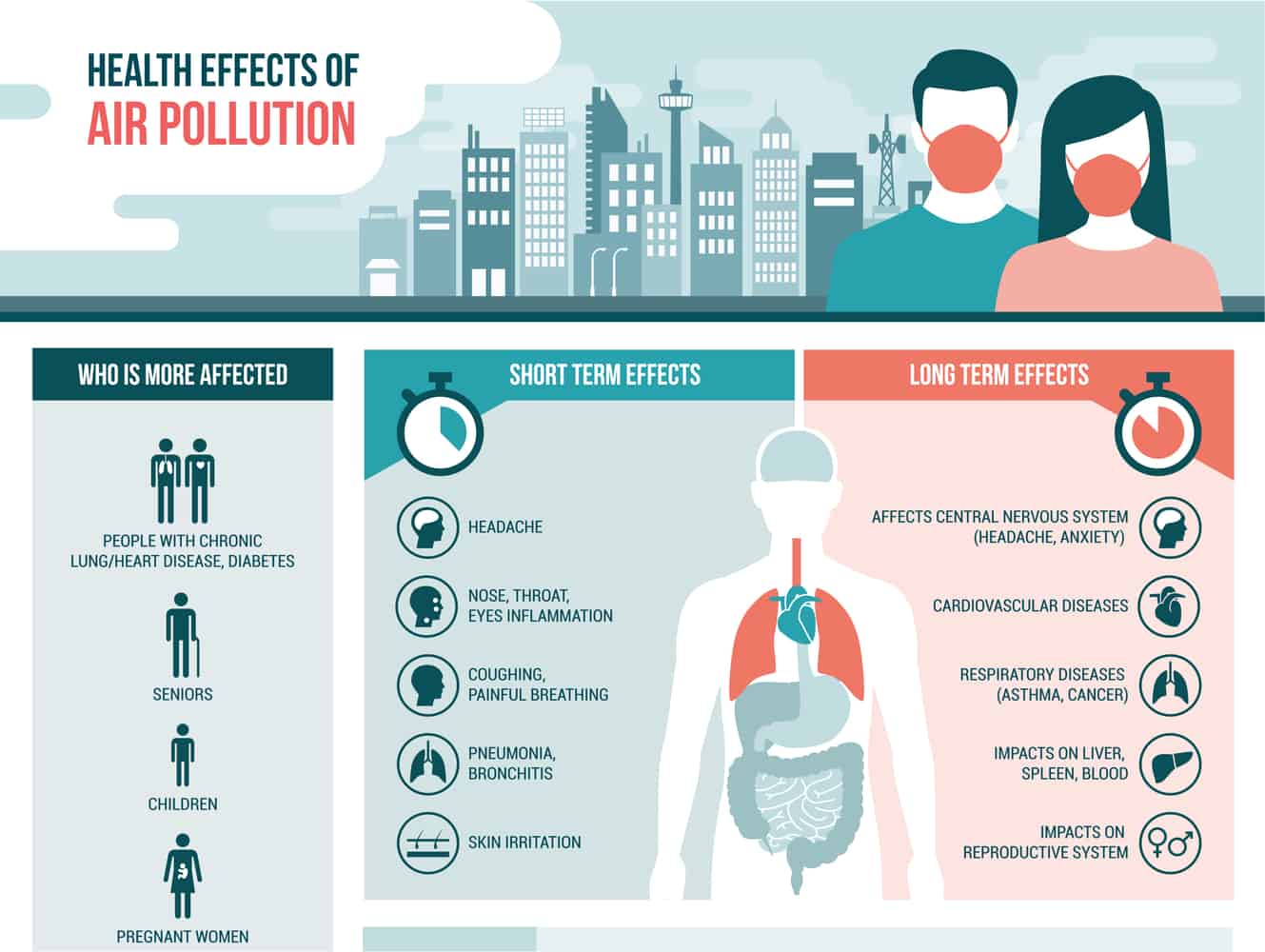
How Important Is Indoor Air Quality To Your Health?
When we say indoor air quality, we are talking about the quality and condition of the air inside of a building, for example our homes, offices and schools. The quality of the indoor air has a direct impact on the satisfaction and well-being of those that live or work inside of that building. Not only does good quality air provide positive health benefits, but in an office, it can also create a better, more productive work environment. Conversely when you have poor quality indoor air, it can start a cycle of health issues that can negatively affect those living and working in the building.
As most people spend much of their time inside, and with increasing concentrations of pollutants found indoors, you may be familiar with some of symptoms. Even short-term exposure can lead to negative side effects. Some pollutants can cause cold- and flu-like symptoms including fatigue, headaches, irritated eyes, and coughing. You may even notice that when you leave the building, your symptoms disappear or lessen. This was certainly the case for me when I was living in a mold and mildew filled college dorm many years ago. I began to realize that my persistent cold-like symptoms would disappear when I went home for winter and summer breaks.
Other pollutants can have a more serious impact with longer term exposure. This can include respiratory diseases, cancer and lung disease. Everyone reacts differently to indoor air pollutants, so it is important to make sure that you have good air quality at work and at home to help reduce your risk of health issues.
This video talks about the dangers of indoor air pollutants in more detail:
Sources of Pollutants in The Home
There are several potential sources of indoor air pollution. Typically, you can trace indoor air pollution back to inadequate ventilation, humidity levels, or to the release of gases / particles.
Here are a few of the main common causes of indoor air pollution:
- Chemicals and odors from household cleaning products
- Cooking and fuel-burning combustion sources
- Tobacco smoke and environmental / secondhand tobacco smoke
- Pets
- Home improvement activities such as painting, sanding, etc.
- Personal care products and air fresheners
- Old building materials including deteriorated insulation which may contain asbestos
- New building materials including upholstery or carpet
- Outdoor pollutants such as radon or pollen which can be carried indoors
Common Household Pollutants
Typically, when you imagine pollution in the air, you think of exhaust coming out of cars or pollution coming out of factory smokestacks. It’s hard to imagine that an even more dangerous pollutant could be hiding inside of your home.
Below is a list of some of the most common household pollutants.

Mold
Mold is a type of fungi that grows both indoors and outdoors and thrives in damp environments. Problems arise when the mold creates microscopic spores which are released into the air we breathe. These mold spores can trigger allergic reactions, including skin irritation, headaches, wheezing, coughing, swelling, throat and eye irritation, and nasal stuffiness.
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Volatile Organic Compounds are commonly found in household cleaners, paints, glues and air fresheners. VOCs include chemicals like formaldehyde, benzene, methylene and chloride, and they can cause damage to your health when these chemicals evaporate at room temperature.
Pet Dander
Pet dander is shed from animals with fur, and it is very tiny and therefore difficult to remove from the air. Pet dander can be a major trigger for allergies and asthma. Common symptoms include itchy eyes, eczema, rash, sneezing, congestion and coughing.
Dust Mites
Dust mites are microscopic living particles that are too small to be seen. They are tiny animals (or mites) that thrive in bedding, carpets, stuffed toys and upholstered furniture and they thrive in damp environments. Dust mites are one of the leading causes of asthma, allergies and eczema.
Biological Contaminants
Biological contaminants include viruses, bacteria, dander, dust, mites, cockroaches, and pollen. These tend to be carried by people and animals into the home, and they thrive and multiply in damp environments. You can keep biological contaminants under control by controlling the humidity levels in your home. The ideal humidity level for a house is somewhere between 30% – 45%.
Secondhand Smoke
Also known as environmental tobacco smoke, secondhand smoke is the smoke produced by burning tobacco products. Tobacco smoke contains more than 7,000 chemical ingredients, hundreds of which are toxic and some which can cause cancer. Even short-term exposure can cause throat, nose, and eye irritations. Long term exposure can lead to lung cancer, bronchitis, pneumonia, and wheezing, similar to what you can develop if you were the smoker yourself.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
An invisible and odorless gas, carbon monoxide is created by an incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, for example from fuel burning appliances. When you are exposed to carbon monoxide, it can cause breathlessness, increased heart rate, confusion, nausea, dizziness, headaches, and tiredness. With a high enough concentration of carbon monoxide exposure can lead to death, even with just a short-term exposure.
Radon
A colorless and odorless gas, radon can be found everywhere at low levels. Radon occurs naturally when uranium in the soil or water breaks down. Exposure to high levels of radon can cause a persistent cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest pains, and can increase your chances of developing lung cancer. In fact radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
Nitrogen dioxide is a corrosive and toxic gas. Not to be confused with nitrous oxide, the laughing gas administered by a dentist. The primary source of nitrogen dioxide in the house is improperly vented combustion appliances, like a gas stove. Nitrogen dioxide can irritate your respiratory tract, nose, eyes, and throat. When you have high exposure to nitrogen dioxide, you can develop a lung injury or pulmonary edema, which is a possibly fatal buildup of liquid in the lungs. Even mild exposure can cause chronic or acute bronchitis, while a low-level exposure may impair lung function for anyone already at risk like asthma sufferers and children.
Lead Particles
The soft and natural metal called lead is actually very lethal if you ingest it. Widely used in paint, lead was banned in 1978. If your home still has paint with lead in it, it can be a dangerous pollutant for your indoor air if lead dust and particles become airborne. Lead exposure can damage your red blood cells, kidneys, nervous system, and your brain. Children that are exposed to lead can experience delayed growth, lower IQ levels, behavioral problems, and short attention spans.
Asbestos
Found unsafe in 1971, asbestos is a group of minerals that are naturally found all over the world. It is actually not a hazardous material when it is intact, it is when the fibers are disturbed that they become airborne and can enter your lungs. With long-term exposure, asbestos can cause breathing problems, permanent lung damage, and diseases like cancer.
Other Factors Affecting Indoor Air Quality
Outside of the normal contaminants you may find in your home, other things can pop up over the years. If you plan to do any remodeling, be prepared for possible air pollutants as a byproduct. Any time you remodel your basement, put in new flooring, hang new cabinets, scrape off paint, or remove wallpaper, you can create a significant source of indoor air pollutants.
Organic solvents like trichloroethane, chloroform, toluene, xylene, benzene, formaldehyde, and asbestos as well as lead dust can be released during a remodel. You have to be extra careful if your house is built before the 1970s, as you could have added environmental problems due to the use of asbestos and lead in construction.
The weather can also have an impact on your indoor air quality. High humidity can cause damp conditions which can lead to mold and mildew growth. This is a very common trigger for allergies and asthma. In contrast, dry air can lead to dry eyes, dry skin, nosebleeds, and cause cracks in furniture and wood floors. So, it is very important for your comfort, health and your belongings to keep humidity levels under control all year round.
Effects Of Indoor Pollution On Our Lives
Health Problems
At home, your family can suffer from health problems caused by indoor air pollution. The very young and very old tend to be the most susceptible, as they spend more time indoors.
Common symptoms caused by indoor air pollution can show up after just a single exposure and include headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and irritated eyes, nose, skin and throat. You might also suffer from allergic reactions, sinus congestion, coughing or wheezing. Certain indoor air pollutants are asthma triggers. These include dust mites, mold and mildew, secondhand smoke, and pet dander. Asthma is alarmingly on the rise in the US, with 750,000 new reported cases of asthma every year.
With high concentrations or extended exposure, indoor pollutants can lead to pneumonia, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), lung disease or cancer.
Research is also being carried out into the impact of poor indoor air quality on student and employee performance. Studies show that your mood, energy level, and concentration can all be affected by poor indoor air quality. If your office or child’s school has issues with air quality, attendance rates and productivity can decline.
HVAC Problems
Your HVAC system’s air filter can also get dirty faster with large amounts of pollutants, which can reduce airflow. Worse, when you have a problem, the HVAC system may actually spread mold, dust, and dirt as well as other contaminants to other areas of your home.
Pollutants will also accumulate in your ductwork reducing airflow. Breakdowns can happen when dirt and dust get into the HVAC system’s inner parts like the compressor and air handler causing you to pay for expensive repairs or even replacements of your system.
Higher Electric Bills
When your ductwork is blocked or your air filter is clogged because of pollutants in your home, your HVAC system will have to work overtime to keep your home at a comfortable temperature. This can affect your electric bill, so make sure to check your ductwork and air filter periodically.
How to Improve Your Indoor Air Quality
Improving the air quality in your home will help you to stay healthy and free of allergies and asthma attacks. While you can’t get rid of all pollutants in your home, you can easily reduce your exposure to many of them with a few simple changes. Here are a few ideas to help you improve the air quality inside your home.
Clean frequently
A clean house can really cut down on animal dander, dust, and mold. I recommend cleaning with non-toxic, no- or low-VOC cleaning products. It is very important to regularly clean areas which are prone to mold (bathrooms, kitchens, basements). It is also important to vacuum all area rugs and carpets one or two times a week using a vacuum with a High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filter.
Also, it is a good idea to clean your bedding regularly, along with drapes and anything else that allergens can cling to. Using dust mite–proof covers on box springs, mattresses, and pillows will also reduce your exposure to allergens when you sleep.
Ventilation
It is very important to increase ventilation in your home by circulating fresh air brought in from the outside. Simply opening windows for a few minutes each day can help improve ventilation in your home. Even when it is cold outside, it’s important to encourage fresh air movement throughout the house by opening some windows. This is especially important when cooking or showering. This can help to remove any odors in the home and to improve stuffy rooms.
Air Purifiers
An air purifier may be a great way to help you if you are allergic to indoor allergens. It is important to purchase a machine with a strong filtration system and a true HEPA filter to effectively target tiny particles in the air. I talk about the benefits of air purifiers and what to look for when shopping in this post.
Dehumidifiers / Humidifiers
A dehumidifier can help stop mold growth by removing excess moisture from the air. I discuss the importance of maintaining ideal humidity levels and rank some of the best dehumidifiers in this post. Basements and bathrooms are susceptible areas for mold growth, so make sure you ventilate them well and remove any visible mold that can collect on the walls or fixtures.
On the other hand, when the air is too dry you could experience discomfort from dry skin, eyes, and nasal passages. Dry nasal passages can make you more susceptible to colds, asthma and allergy flare ups. So, it’s equally important to ensure your house has enough moisture, especially in the winter months when we turn on the heat which can dry out our air. During these times it’s helpful to add a humidifier to maintain the optimal humidity levels inside your home. I discuss the benefits of installing a whole house humidifier here.
Change Filters Regularly
Anyone with a forced-air heating system will want to change the filters frequently. These filters will help to guarantee that airborne irritants like dust will get trapped instead of finding themselves traveling throughout the house. You may also want to consider having your ducts cleaned to remove dust that might be trapped.
Air Purifying Plants
Studies show that indoor plants can help to purify the air by removing some chemicals from the air. However, it is very important to not over water your houseplants. This can lead to mold growth, which can trigger allergic reactions.
The following video talks about some more solutions to improving your indoor air quality.
Conclusion
Improving your indoor air quality will save you money and your health. When you are exposed to smoke, mold, mildew, dust, and dirt, it is going to have a negative effect on your health. Make sure to take steps to reduce your exposure to contaminants in your home to not only improve your lifestyle but also to reduce your bills.
For more like this, check out our latest posts on Humidity Control (Humidifiers & Dehumidifiers) and Air Purifying.